Perfectly Inelastic Collision Examples
This study investigated the collapse capacity of inelastic single degree of freedom sdof systems subjected to mainshock aftershock earthquake sequences.

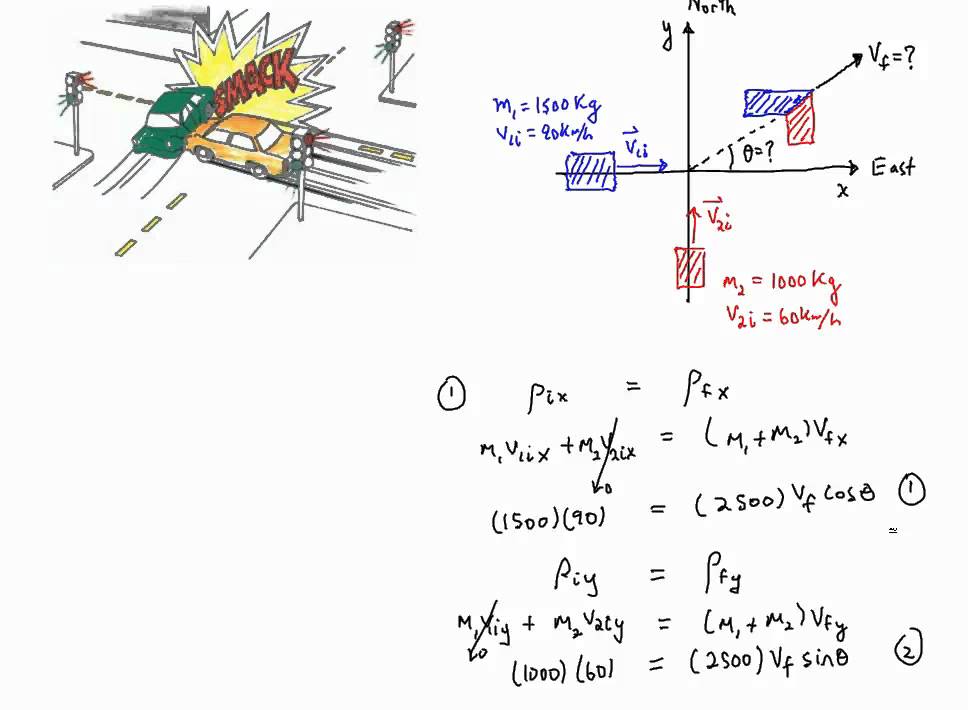
Perfectly inelastic collision examples. A collision is the event in which two or more bodies exert forces on each other in about a relatively short time. Although the most common colloquial use of the word. An inelastic collision is any collision between objects in which some energy is lost. A special case of this is sometimes called the perfectly inelastic collision.
A collision is an isolated event in which two or more colliding bodies exert relatively strong forces on each other for a relatively short time. The procedure for analyzing a collision depends on whether the process is elastic or inelastic. Kinetic energy is conserved in elastic collisions whereas kinetic. Collisions can be elastic or inelastic.
Learn about whats conserved and not conserved during elastic and inelastic collisions. Inelastic collisions occur when objects collide and energy is lost during the collision. That is s ke before s ke after. During perfectly inelastic collisions.
It might be tempting to confuse momentum with another physical concept inertia. Inertia as defined by the second law of motion is the.




























:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/158683920-56a72bcb5f9b58b7d0e78a3a.jpg)














